Trace Heating
Heat tracing systems are used wherever stored and transported materials cannot be adequately protected against heat loss by insulation. Heat tracing is a heating system that is installed along pipelines, tanks or other system components to protect them from frost damage or to maintain process temperatures.
In combination with insulation, electric trace heating provides an efficient and reliable solution for temperature maintenance and frost protection in various applications. This not only ensures the safety of the process, but also prevents damage to the system.


Heating Tapes
Self Limiting Tapes
Self-limiting heating cables ensure frost protection or temperature maintenance for pipes, tanks and similar installations. It is approved for use in hazardous, industrial and demanding environments.
- Temperature resistant up to 250°C
- Output power up to 120W/m
- No overheating with overlapping
- Easy to cut to length on site

Constant Wattage Heating Tape
- Temperature resistance up to 425°C
- Output power up to 150W/m
- Easy to cut to length on site



Heating Cables
Single Core Heating Cable
- Temperature resistant up to 260°C
- High rated voltage of up to 450/750V
- Output cable up to 25W/m
- Heating circuit lengths >250m can be realized

Mineral Insulated Heating Cable
- Temperature resistant up to 650°C
- Rated voltages up to 500V
- High chemical resistance


Connection Systems
Heating Tape Connection Set
- Temperature resistant up to 200°C
- Can be used flexibly
- Compact design

Heating Cable Connection Set
- Temperature resistant up to 200°C
- Compact dimensions
- Rated current up to 98A
Junction Box
- Compatible with all connection systems
- Temperature resistant
- Antistatic
- Corrosion and UV resistant
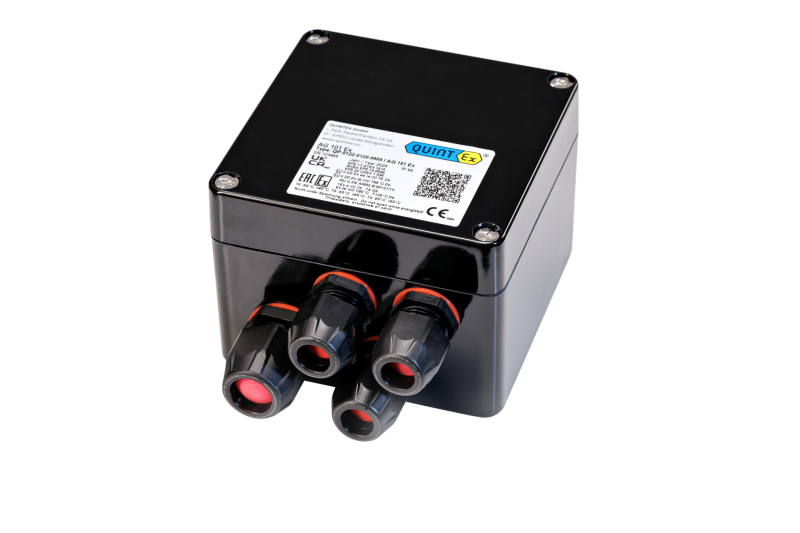

New Product: Junction Box AG 2..
Glass fiber reinforced polyester enclosure for use in hazardous area for connecting self-limiting heating cables, single-core heating cables and mineral-insulated heating cables.
Thanks to the pre-installed mounting adapter, the supplied 3- or 5-pole Ex e Wago terminals can be mounted flexibly and without the need for tools
- Compatible with all termination systems
- Variably equippable
- Easy tool-free installation
- Corrosion-resistant and UV-resistant
- Flexbility through modular design
> 1 enclosure > multiple connection options with terminal set



Controller
Mechanical Controllers
- Switching capacity up to 25A
- Different temperature setting ranges
- Compact design
- UV-resistant housing

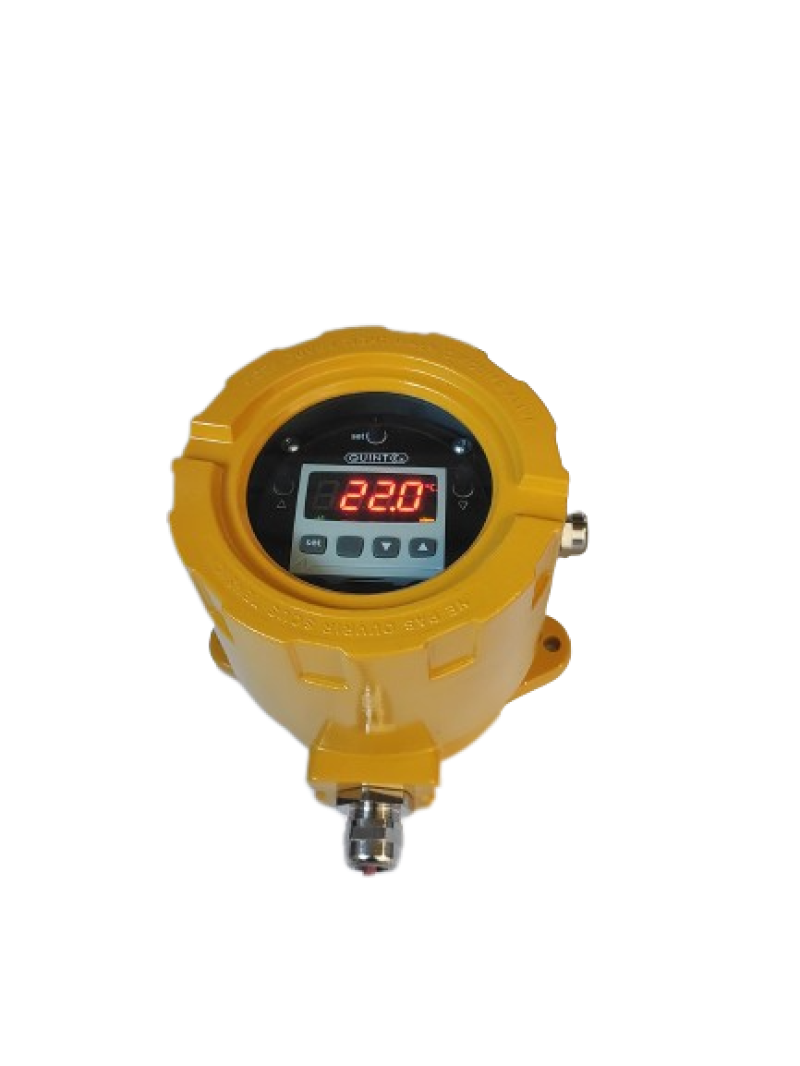
Electronical Controllers
- Measuring range up to 800°C
- Alarm signal
- available with Wifi & Bluetooth



Heating Devices
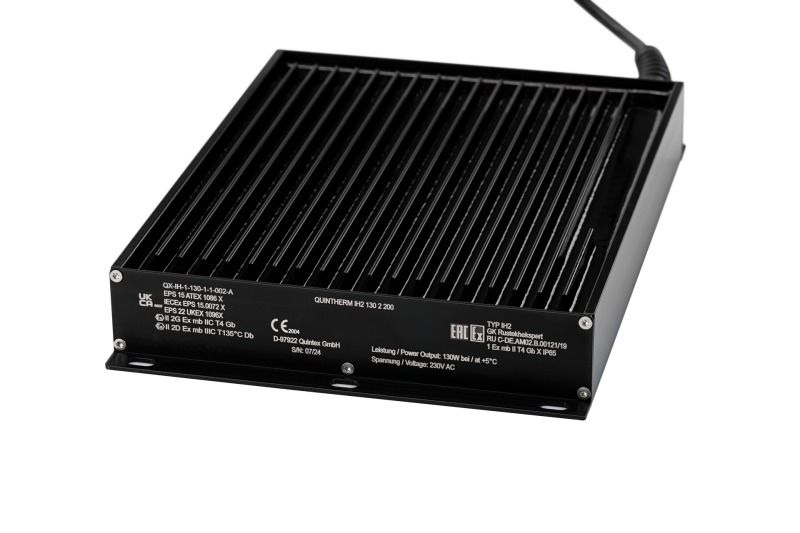
Heating Plate
- Self-limiting characteristic
- Rated power up to 1000W
- Compact dimensions

Motor Anticondensation Heater
- Self-limiting characteristic
- max. temperature resistance up to 180°C
- Compact dimensions
Accessories



Commercial + Construction
Heating Tapes
- Different output capacities
- No overheating with overlapping
- Easy to cut to length on site
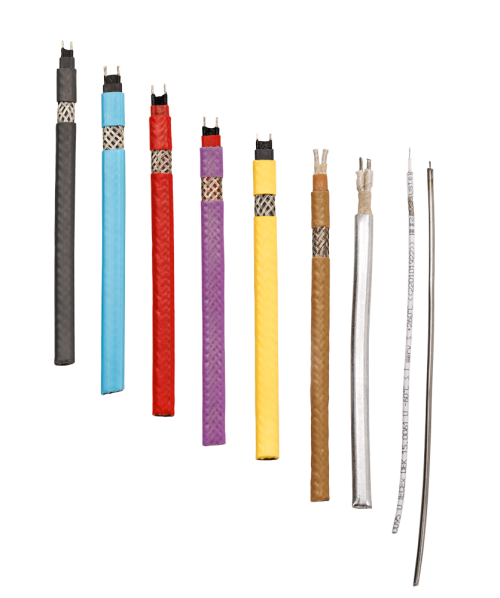

Connection Systems
- Flexible application
- Compact design
- Quick to assemble

Plug-and-Play Heating Circuit
- Heating circuit including frost protection thermostat
- No overheating with overlapping
- Simple installation
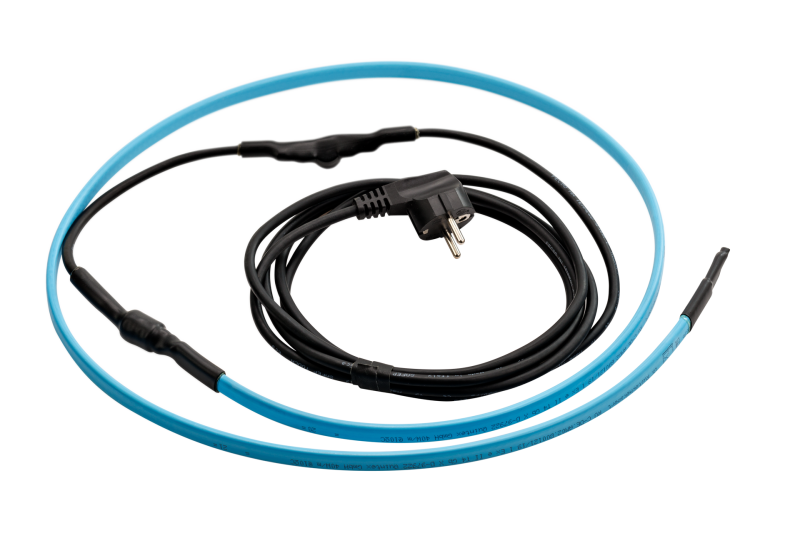

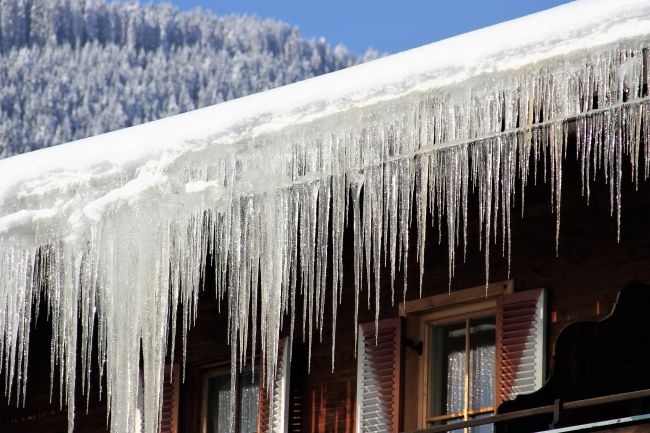
Gutter Heating Circuit
- High UV resistance
- Can be cut to length individually on site
- Prevention of damage to roof and building

Pond Heater
- Plug-in pond heater
- Preset control unit
- Simple installation
Control Units
- Compatible with all heating systems
- Simple installation
- Switching capacities up to 25A
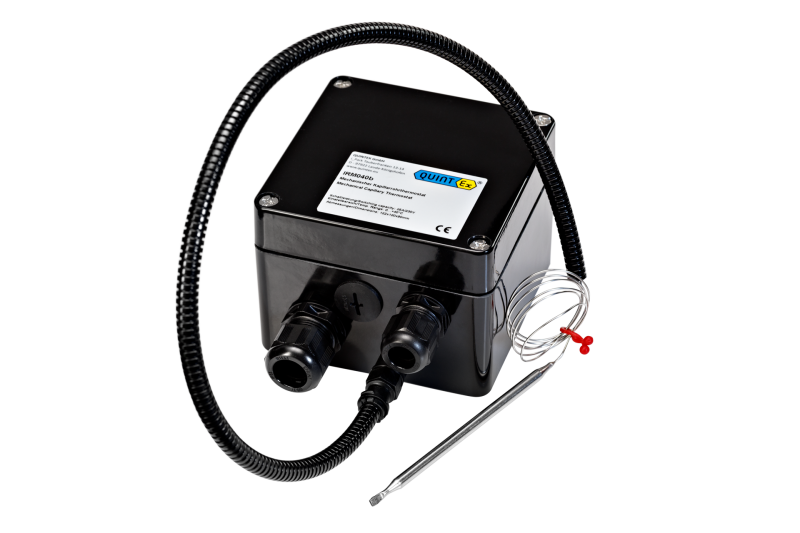



General Information
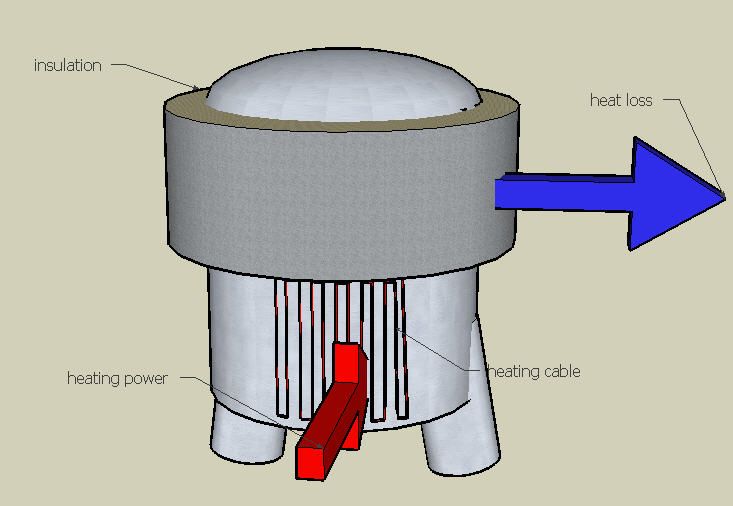
Heat Loss
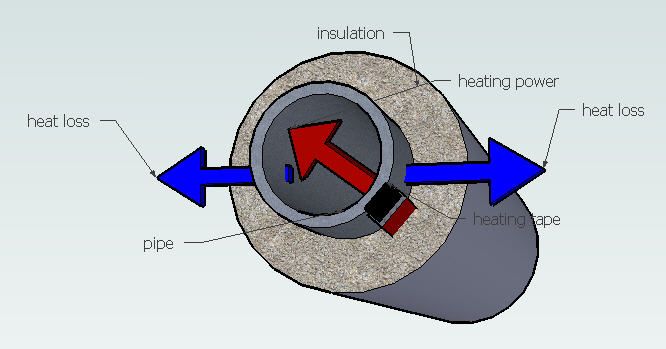
Qv= (2 * pi * lambda * (Th - Tmin)) / (ln * (D/d))
Qv heat loss(W/m)
lambda thermal conductivity(W/mK)
Th maintain temperature (°C)
Tmin minimum ambient temperature (worst case °C)
ln natural logarithms
D pipe diameter with insulation(mm) (pipe diamter+ 2 x insulation thickness)
d outer pipe diamter without insualtion(mm)
the formula to calculate the heat loss of a tank it similar:
Qv= (A * lambda * (Th - Tmin)) / s
Qv= total heat loss(W)
A = total tank surface ( m²)
s = insulation thickness (meter!)
(all other see above)
Thermal Insulation

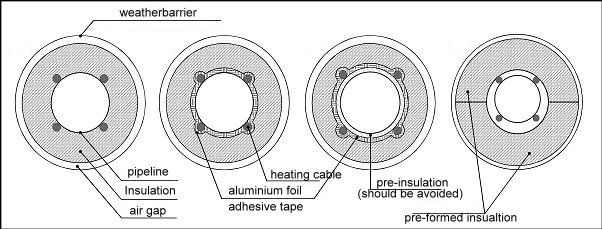
Thermal insulation plays a crucial role in a trace heating system as it helps to maximize the efficiency of the system and minimize heat loss. Effective thermal insulation helps to keep the heat generated where it is needed and prevents unnecessary heat loss to the environment.
The correct selection and installation of thermal insulation is therefore crucial to meet the heat-tracing requirements and ensure efficient thermal insulation.
The following points should be considered when selecting insulation:
- Thermal properties
- Mechanical and chemical resistance
- Moisture resistance
- Flammability